Artificial Intelligence (AI) is no longer a futuristic concept confined to science fiction. It’s an integral part of our daily lives, silently shaping how we interact with technology. From personalized shopping experiences on platforms like Amazon to conversational AI tools like Siri and Alexa, AI applications are everywhere. But what exactly is AI, how does it work, and what opportunities and challenges does it present?
This blog offers a comprehensive introduction to AI for beginners, breaking down complex concepts such as machine learning, ethical considerations, and current applications into easy-to-understand language. We’ll also explore practical resources for enhancing your understanding of AI, including specialized courses from Learning Tree. At the end, you’ll have a solid grasp of Artificial Intelligence and its potential impact on modern life.
For a deeper introduction, explore Learning Tree’s Introduction to Artificial Intelligence (AI) course.
What Is Artificial Intelligence and How Does It Work?
Artificial Intelligence refers to systems or machines designed to mimic human intelligence, whether by learning through experience, recognizing patterns, or making data-informed decisions. It can range from simple systems like recommendation algorithms to more advanced applications like self-driving cars.

At the heart of Artificial Intelligence lies machine learning—a process where AI systems analyze and learn from data, improving their performance over time. Traditional programming requires explicit instructions, but AI systems built on machine learning adapt and evolve independently through these steps:
- Data Collection: Large datasets—like images, text, or video—are gathered to train the system.
- Pattern Recognition: The AI identifies relationships and patterns within the data.
- Optimization: The system adjusts to improve accuracy.
- Deployment: Once trained, the model can handle new data and tasks while continuing to learn.
For a hands-on exploration of this foundational AI technology, check out Learning Tree’s Data Science Training with Python course.
Types of AI and Their Real-World Applications
Artificial Intelligence can be categorized into Narrow AI and Artificial General Intelligence (AGI):
- Narrow AI specializes in single tasks. Examples include AI chatbots and algorithms used to detect medical conditions from imaging. This type of AI is what powers most AI applications currently in use.
- Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), on the other hand, refers to a hypothetical AI capable of human-like versatility. AGI systems, still theoretical, would adapt to new tasks across multiple domains without specific training.
How Does AI Work?
Traditional programming involves feeding a computer explicit step-by-step instructions, but machine-learning takes a different approach - allowing computers to learn from data without being explicitly programmed.
Let's take a quick overview of how it works:
- Training data is fed into a machine-learning algorithm. This data trains the system, e.g., labeled images to teach a system to recognize cats.
- The algorithm analyzes the data to find patterns and relationships, adjusting its internal parameters to optimize pattern detection.
- Now that it's optimized, the model can predict or decide things using new, unseen data.
- Over time, the system continues to learn from new data to improve its model.
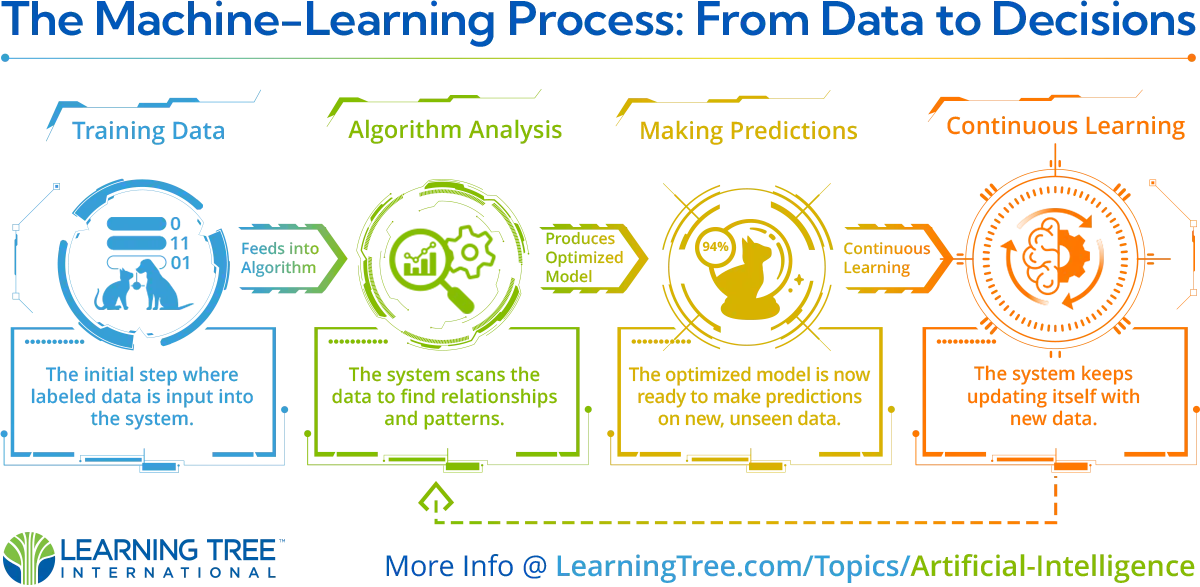
This iterative approach allows machines to learn and improve without explicit programming. Neural networks, illustrating elements of human brain functionality, are adept at discerning patterns and distinct features within data. Notably, deep learning—a specialized sub-field of machine-learning—has gained considerable recognition and progress, propelled by the advent of vast computational resources. The enhancements in both neural networks and machine-learning are pivotal contributors to the recent rise of AI applications. Such networks empower machines to emulate human decision-making processes.
Everyday Examples of AI Applications
AI has integrated itself into numerous industries, impacting how businesses operate and how individuals interact with technology. Here are a few examples:
- Healthcare: AI systems analyze medical data to assist in early diagnosis and treatment planning.
- Cybersecurity: Machine learning models monitor and detect potential cyber threats in real time. Want to explore cybersecurity further? Discover Learning Tree’s AI Cybersecurity Training.
- Communication: Natural language processing (NLP) enables more human-like interactions in tools like chatbots and virtual assistants. For practical skills in this area, enroll in Learning Tree’s Practical Skills in NLP and Generative AI.
- Data Analysis: AI simplifies large-scale data analysis, delivering insights and improving decision-making processes.
For those intrigued by data-driven AI solutions, Learning Tree’s Graph Databases for Data Analytics and AI course is an excellent starting point.
Addressing Ethical Challenges in AI Development
While AI offers remarkable capabilities, its development raises several ethical questions:
Common Concerns:
- Perspective Awareness in AI Models
AI learns from data—if this data reflects societal biases, the AI outputs may perpetuate these inequalities. For example, AI systems used in hiring processes have faced scrutiny for unintentional Opportunity Gaps.
- Lack of Transparency
Many AI models function as "black boxes," making it difficult to understand how decisions are made.
- Security Risks
The more powerful AI becomes, the greater its potential misuse in cyberattacks. This is why understanding secure and responsible AI practices is essential.
Building Ethical AI Systems
- Varied Data Sets
Ensuring that datasets include a wide range of variables improves fairness in AI decision-making.
- Regulation and Oversight
Policies and industry guidelines can enforce ethical usage, steering AI development toward equitable outcomes.
Dive deeper into creating responsible AI systems by exploring Learning Tree’s Automating Prompt Engineering with Python course.
What is model collapse?
Model collapse can happen quickly, sometimes as early as the second or third round of model training. It happens when a machine-learning model starts learning from other AI outputs instead of real human data, making the results less reliable. Think of it like making copies of a picture until you can't recognize the original anymore. Eventually, the first-Career Stages learning data is purged and replaced with blurry copies to make new Career Stages.
What is model drift?
Model drift is an intriguing phenomenon that affects the accuracy of AI systems. Let's dive into a few reasons why this might happen:
- Environmental Shifts: Just as changing seasons can alter the landscape, shifts in the environment can impact a model's performance. Imagine an AI trained to predict the weather. If there's a significant change in the climate over the years, our trusty AI might not be as spot-on with its forecasts.
- Evolving Relationships: Over time, the dynamics between certain variables may evolve - a phenomenon known as concept drift. Consider an AI model gauging consumer product demand. Our model's predictions may not align with actual outcomes if societal trends alter buying behaviors.
- Data Collection Modifications: Sometimes, the method of collecting data or its unit might change, causing a model to misinterpret information. For instance, if a system learns from weight data in kilograms and suddenly receives input in grams, there's bound to be some confusion.
Think of how a cherished photo of your young pet might not resemble them as they grow older. Similarly, a model can stray from accuracy if the variables it was trained on evolve. To maintain reliability, continuous updates and refinements are essential in AI models.
The Future of AI
Artificial Intelligence continues to evolve, showing potential for unprecedented growth. Key areas of future focus include:
- Personalized Experiences
AI is expected to further enhance individualized experiences in healthcare and education. For example, adaptive learning platforms can tailor resources to suit each student’s needs.
- Automation
Routine tasks in industries like manufacturing and logistics will become fully automated, increasing efficiency while reducing costs.
Risks to Anticipate
With these advancements come risks that require proactive solutions:
- Job Displacement
Automation threatens to disrupt traditional job roles. Policies focused on upskilling displaced workers are critical.
- Ethical Dilemmas
Striking a balance between innovation and responsible use will remain a priority.
By staying informed about these developments, individuals, and organizations can plan effectively for the AI-driven future. For an overview of AI’s applications across industries, consider Learning Tree’s Practical Skills in NLP and Generative AI.
The Takeaway
Artificial Intelligence is transforming industries, solving complex problems, and opening up new possibilities. However, understanding its core principles, capabilities, and challenges is crucial to leveraging its full potential responsibly.
If you’re inspired to expand your AI knowledge, Learning Tree offers comprehensive courses tailored to beginners and professionals alike. From foundational AI skills to advanced applications in cybersecurity and data science, these courses will guide you in applying AI effectively in your career.
Begin your AI learning journey today with Learning Tree’s AI Training Catalog and AI Workforce Solutions. Equip yourself with the tools and knowledge to succeed in an AI-driven world.


